
What is Smart manufacturing? Everything You Need to Know About That
Industries & Technologies
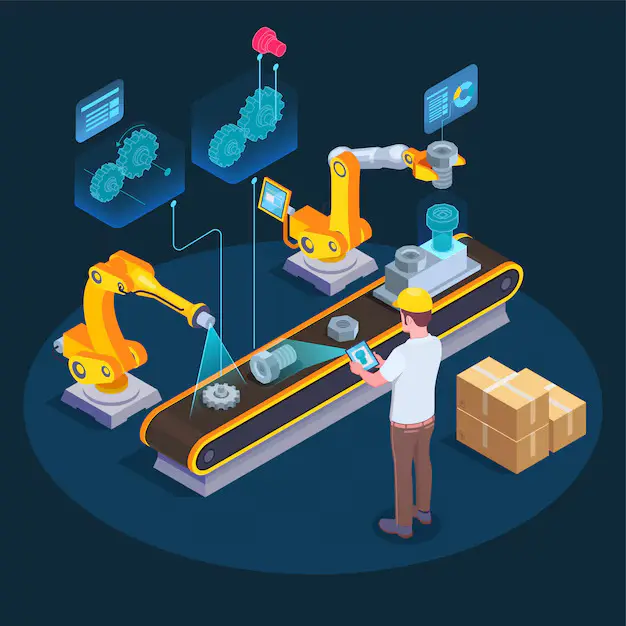
Smart Manufacturing is a modern production strategy that harnesses digital technologies, automation, and data-informed processes to improve manufacturing effectiveness, versatility, and Eco-friendliness. It merges the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, big data analytics, and cloud computing to develop intelligent and interconnected production facilities.
The technologies driving this change are full of potential, and we can’t wait to dive deeper into this topic with you in the article ahead!
Benefits of Smart Manufacturing:
- Increased Efficiency – Reduced downtime and optimized resource use.
- Higher Quality – AI-driven defect detection improves product consistency.
- Cost Savings – Predictive maintenance reduces unexpected failures.
- Flexibility & Customization – Easier adaptation to market changes and customer demands.
- Sustainability – Energy-efficient processes and reduced waste.
Key Features of Smart Manufacturing:
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) – Sensors and connected devices collect real-time data from machines, products, and supply chains.

- AI & Machine Learning – Predictive maintenance, quality control, and demand forecasting using AI algorithms.
- Automation & Robotics – Collaborative robots (cobots) and autonomous systems improve precision and reduce labor costs.
- Big Data & Analytics – Data-driven insights optimize production schedules, reduce waste, and improve efficiency.
- Digital Twins – Virtual models of physical systems simulate and optimize manufacturing processes.
- Cybersecurity – Protecting smart factories from cyber threats with advanced security measures.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) – Enables rapid prototyping and customized production.
- Cloud & Edge Computing – Real-time processing and storage of manufacturing data.
Examples of Smart Manufacturing Applications:
- Predictive Maintenance – AI detects machine failures before they happen.
- Smart Supply Chains – Real-time tracking of materials and inventory.
- Autonomous Factories – Lights-out manufacturing with minimal human intervention.
- Digital Thread – End-to-end traceability of product lifecycle.
Smart Manufacturing is a core component of Industry 4.0, transforming traditional factories into intelligent, adaptive, and highly efficient production systems.